Criticisms aimed at the perceived centralization of Ethereum (ETH) staking pools may finally be quelled by an alternative staking infrastructure that aims to improve private key security and reduce validator down times and slashing penalties.
Speaking exclusively to Cointelegraph, SSV.network founder Alon Muroch outlined how the platform’s distributed validator technology (DVT) developed in partnership with the Ethereum Foundation will help decentralize ETH staking pools and validators.
SSV.network launched its public mainnet with more than 10 staking decentralized applications deploying their platforms on the network on Sept. 14. DVT is envisaged to decentralized the current landscape of staking providers, which is currently dominated by a handful of ETH staking pools that command a significant share of ETH locked in the ETH2 staking contract.
Related: SSV launches $50M ecosystem fund to support ETH staking tech
According Muroch, the technology is an approach to validator security that spreads out key management and signing responsibilities across multiple parties, reducing single points of failure and increasing validator resiliency.
The technology splits a private key used to secure a validator across a cluster of computers. This increases security and allows for some nodes of a validator cluster to go offline, which also reduces single points of failure from the network and makes validator sets more robust.
“By splitting keyshares between a diverse set of nodes in a cluster, validators become much more decentralized. Staking pools that use DVT can decentralize their own infrastructure or delegate it to SSV.network node operators.”
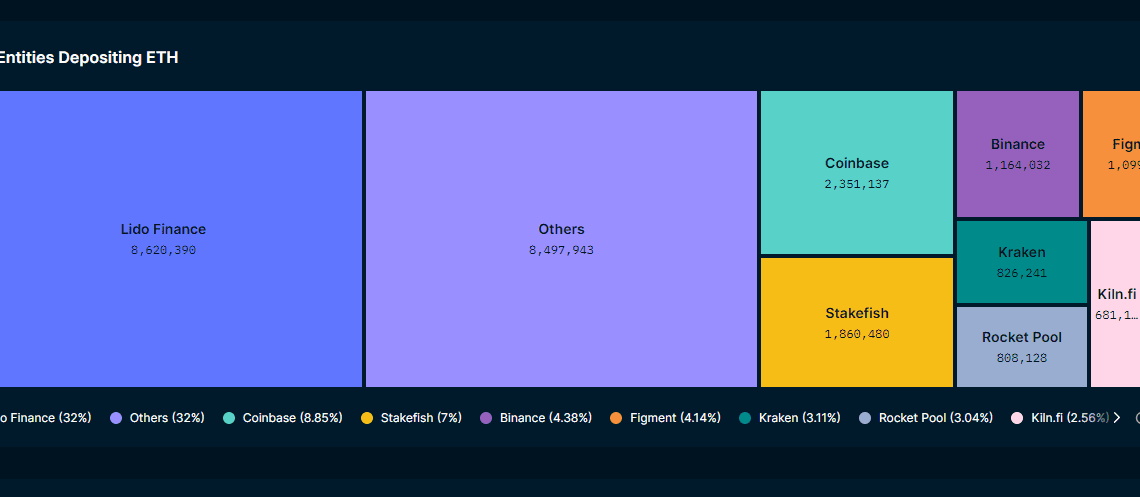
Data from blockchain analytics firm Nansen shows that Lido Finance accounts for 32% of ETH locked in the Beacon Chain deposit contract. ETH staking pools offered by Coinbase (8%) and Binance (4%) also command a significant share of staked ETH.
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Cointelegraph.com News…