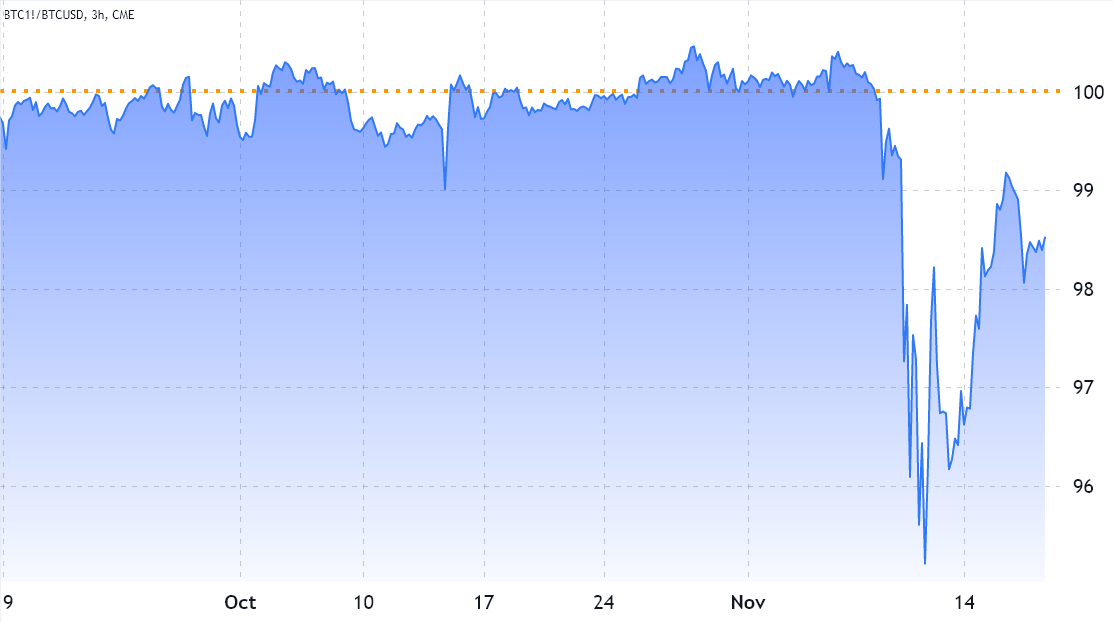
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) Bitcoin (BTC) futures have been trading below Bitcoin’s spot price on regular exchanges since Nov. 9, a situation that is technically referred to as backwardation. While it does point to a bearish market structure, there are multiple factors that can cause momentary distortions.
Typically, these CME fixed-month contracts trade at a slight premium, indicating that sellers are requesting more money to withhold settlement for longer. As a result, futures should trade at a 0.5% to 2% premium in healthy markets, a situation known as contango.
However, a prominent futures contract seller will cause a momentary distortion in the futures premium. Unlike perpetual contracts, these fixed-calendar futures do not have a funding rate, so their price may vastly differ from spot exchanges.
Aggressive sellers caused a 5% discount on BTC futures
Whenever there’s aggressive activity from shorts (sellers), the two-month futures contract will trade at a 2% or higher discount.
Notice how 1-month CME futures had been trading near the fair value, either presenting a 0.5% discount or 0.5% premium versus spot exchanges. However, during the Nov. 9 Bitcoin price crash, aggressive futures contracts sellers caused the CME futures to trade 5% below the regular market price.
The present 1.5% discount remains atypical but it can be explained by the contagion risks caused by the FTX and Alameda Research bankruptcy. The group was supposedly one of the largest market makers in cryptocurrencies, so their downfall was bound to send shockwaves throughout all crypto-related markets.
The insolvency has severely impacted prominent over-the-counter desks, investment funds and lending services, including Genesis, BlockFi and Galois Capital. As a result, traders should expect less arbitrage activity between CME futures and the remaining spot market exchanges.
The lack of market makers exacerbated the negative impact
As market makers scramble to reduce their exposure and assess counterparty risks, the eventual excessive demand for longs and shorts at CME will naturally cause distortions in the futures premium indicator.
The backwardation in contracts is the primary indicator of a dysfunctional and bearish derivatives market. Such a movement can occur during liquidation orders or when large players decide to short the market using derivatives. This is especially true when open interest increases…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Cointelegraph.com News…