Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been growing at an unprecedented rate in recent years and is being integrated into a range of industries. But its rapid growth has sparked concern over job losses, as many tasks previously performed by humans could soon be automated by AI.
For example, on May 1, IBM CEO Arvind Krishna told Bloomberg that 7,800 jobs at the firm could be replaced by AI and automation over the next five years, which represents approximately 30% of its workforce.
While AI has the potential to improve efficiency, increase productivity and reduce costs, the rapid advancements seen in tools such as ChatGPT-4 — which is a huge improvement on its predecessor ChatGPT-3.5 — have many people concerned that their industry will be one of those hit hardest by related job losses.
ChatGPT and other Large Language Models (LLMs) can already be used to complete a variety of tasks, such as generating smart contract code, community management, market analysis and more.
A research report from professional services firm Accenture released in March referred to ChatGPT’s “explosive popularity” as “AI’s first true inflection point in public adoption,” adding:
“Nearly every job will be impacted — some will be eliminated, most will be transformed, and many new jobs will be created.”
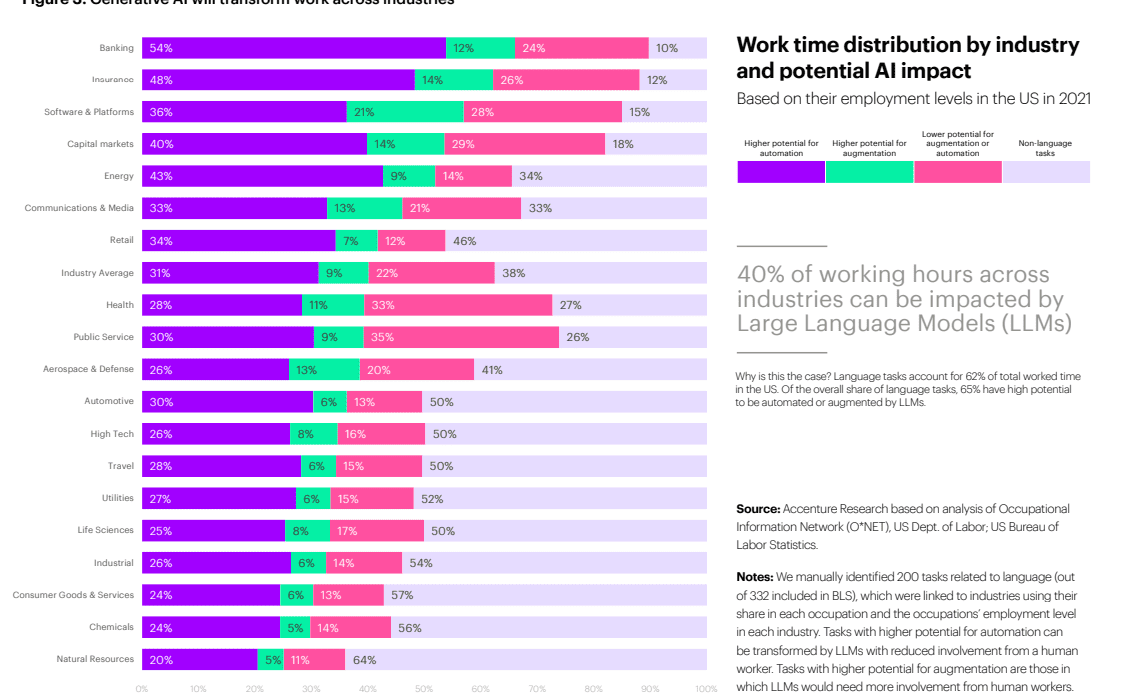
Accenture’s research found that 40% of working hours across different industries could be affected by LLMs, and identified banking as the industry most likely to be affected as 54% of tasks were found to have a high potential for automation, closely followed by insurance at 48%.
Replacement and synthesis
Cointelegraph asked Dr. Gary Marcus, an AI entrepreneur and author of the book Rebooting AI: Building Artificial Intelligence We Can Trust, what he thought about AI’s impact on various industries.
Marcus suggested that commercial artists may be most at risk, which refers to branding, logos, advertising and graphic design — generally just art used for commercial purposes.
This is distinct from fine art, which refers to paintings, sculpture and photography — art that is more likely to be displayed at art museums such as the Louvre and are much harder for AI to create.
Marcus downplayed the prospect of job losses in the short term, however, noting that “in many cases people will work together with machines, at least for [the] next several years.”
When asked how people can best…
Click Here to Read the Full Original Article at Cointelegraph.com News…